Building a Future-Ready India
India’s 2025 Economic Reforms mark a decisive shift towards outcome-driven governance, where the focus is no longer on expanding rules but on delivering measurable results. From simplified taxation and GST 2.0 to four unified Labour Codes, stronger MSME support, expanded rural employment guarantees, and a landmark Export Promotion Mission, these reforms aim to make India future-ready, inclusive, and globally competitive.
Designed around the principles of ease of doing business, ease of living, and long-term resilience, the reforms reduce compliance burdens, strengthen social protection, enhance policy certainty, and empower citizens—especially youth, women, small businesses, and rural communities. Together, these initiatives reflect a mature economic vision focused on growth with trust, speed with transparency, and development with dignity.
- Next-Gen GST simplified taxation, expanded the taxpayer base to 1.5 crore.
- The Export Promotion Mission (₹25,060 crore) enhances support for MSMEs and first-time exporters, providing finance, compliance, and market access.
- Rural employment reforms provide 125 days of guaranteed paid work.
Setting the Stage: India’s 2025 Economic Vision

Economic reforms in 2025 reflect a maturing phase of India’s governance, where the emphasis shifted decisively from “expanding regulatory frameworks” to “delivering measurable outcomes”. The focus moved towards simplifying systems, reducing compliance burdens, and improving predictability for citizens and businesses. Across taxation, GST, labour regulation, and business compliance, reforms were designed to make every day economic interactions smoother, faster, and more transparent, strengthening trust in institutions and policy certainty.
The year’s initiatives emphasized ease of living, ease of doing business, and inclusive growth, aligning regulatory structures with India’s evolving economic aspirations. From simplified tax regimes and Next-Generation GST to modern labour codes and expanded MSME definitions, the Government ensured that reforms not only reduced friction in everyday economic activities but also empowered youth, women, small businesses, and rural communities. Collectively, these measures illustrate a governance approach rooted in outcome-driven policymaking, fostering trust, predictability, and long-term economic resilience.

Key Reforms Shaping Growth and Opportunity
Income Tax Reforms
In a major relief for Indian families and individual taxpayers, the Union Budget 2025-26 introduced substantial reforms in direct taxation, ensuring that annual incomes up to ₹12 lakh are exempt from income tax under the new regime, with the effective exemption rising to ₹12.75 lakh for salaried taxpayers on account of the standard deduction. This change reaffirmed the Government’s commitment and left millions of middle-class households with higher disposable income, boosting consumption, savings, and investment.
In July 2024, the Government announced a comprehensive overhaul of the Income-tax Act, 1961, leading to the New Income Tax Act, 2025 – a landmark development to simplify language, remove obsolete provisions and consolidate & restructure provisions. An internal Departmental Committee, constituted by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) for a comprehensive review of the existing Act, undertook the reform with three guiding principles:
- Textual and structural simplification, improved clarity and coherence.
- No major tax policy changes, ensuring continuity and certainty.
- No modifications of tax rates, preserving predictability for taxpayers.
The Income Tax Act, 2025 modernizes India’s direct tax framework by simplifying and streamlining tax legislation, making it more accessible, transparent, and less prone to litigation. A key reform is the introduction of a unified “Tax Year – the twelve-month period of the financial year commencing on the 1st April”, replaces the earlier concepts of Assessment Year and Previous Year. It not only improves clarity and makes it easier for taxpayers to understand the financial period their income and tax filings, but also reduces ambiguity in compliance and interpretation.
The Act strengthens digital-first enforcement, faceless tax administration, consolidates compliance provisions such as Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) under a single section, empowers the Government to introduce technology-enabled schemes, and enhances dispute-resolution mechanisms.


Labour Reforms
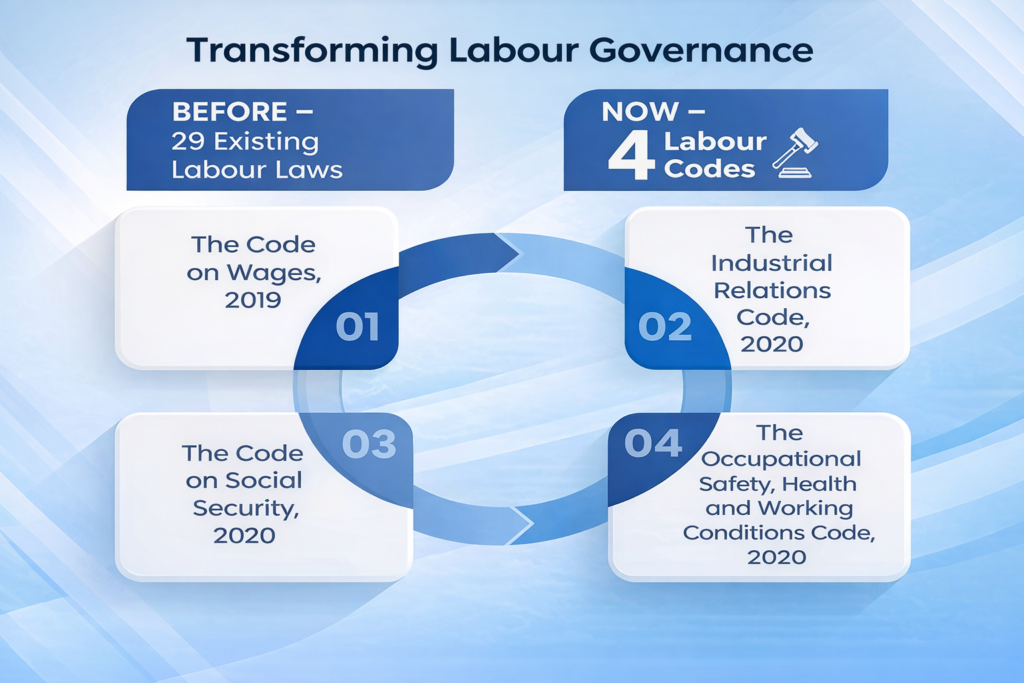
In a landmark reform, the Government of India consolidated 29 existing labour laws into four Labour Codes- the Code on Wages, 2019, the Industrial Relations Code, 2020, the Code on Social Security, 2020 and the Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020.
The new framework enhances ease of doing business while expanding wage security, social protection, and workplace safety for workers, including women, migrant, gig, and platform workers.
- Wages: It aims to strengthen workers’ rights while promoting simplicity and uniformity in wage-related compliance for employers. Uniform definition of wages and statutory minimum wages across sectors, improving income security and reducing disputes.
- Industrial Relations: Simplification laws related to trade unions, conditions of employment in industrial establishments or undertakings, investigation and settlement of industrial disputes.
- Social Security: Extension of social security to all workers– including unorganized, gig, and platform workers-covering life, health, maternity, and provident fund benefits, while introducing digital systems and facilitator-based compliance for greater efficiency.
- Occupational Safety & Health: Safeguarding worker rights and safe working conditions, and creating a business-friendly regulatory environment.
The reforms expand the safety net for India’s workforce, with nearly 10 million Gig and Platform workers receiving annual social security support. Women workers benefit from assured leave provisions, maternity benefits and improved workplace safety. Overall, the Labour Codes mark a decisive shift from rule-heavy regulation to outcome-based governance, creating one unified framework for over 50 crore workers across sectors. Additionally, the codes lay a strong foundation for a future-ready workforce and resilient industries aligned with India’s long-term growth aspirations.

Rural Employment Reforms
Rural employment reforms anchored in the enactment of the Viksit Bharat – Guarantee for Rozgar and Ajeevika Mission (Gramin) Act, 2025, replaces the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) with a modern statutory framework that enhances livelihood security and integrates employment with community development.
- Extended Employment Guarantee: 125 days of wage employment per rural household in a financial year.
- Integrated Provision for Agriculture and Rural Employment: facilitate adequate availability of agricultural labour during peak sowing and harvesting seasons while ensuring a calibrated balance that supports both agricultural productivity and worker security.
- Timely Wage Payments: timely payment of wages on a weekly basis or, in any case, within fifteen days of completion of work, reinforcing wage security and protecting workers from delays.
- Asset Creation Focus: Work contributes creation of durable public assets across four priority thematic domains – water security & related works, rural infrastructure, climate-resilient projects, and livelihood enhancement.
- Decentralized Planning: All works flow from Viksit Gram Panchayat Plans (VGPPs), prepared through participatory processes at the Gram Panchayat level and approved by the Gram Sabha. These plans are digitally integrated with national platforms including PM Gati Shakti, enabling convergence across Ministries while retaining decentralised decision-making.
- Financial Architecture: The Act is implemented as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, notified and operationalised by State Governments in accordance with its provisions.
- Strengthened Administrative Capacity: The administrative expenditure ceiling has been increased from 6% to 9%, strengthening staffing, training, technical capacity, and field-level support to improve institutional delivery and outcomes.

Ease of Doing Business Reforms
To ensure that Quality Control Orders (QCOs) do not disrupt domestic production, the Government has implemented them in a phased and MSME-friendly manner through the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).

Quality Control Orders (QCOs) – Key Relaxations: Additional compliance time was given to Micro (6 month) and Small (3 months) enterprises, exemptions were provided for export-oriented and R&D imports (upto 200 units), and legacy stock could be cleared within six months, easing the transition for businesses.
Under BIS Support Measures for MSMEs, enterprises received concessions on annual marking fees, the in-house laboratory requirement was made optional with access to accredited or shared labs, inspection and testing processes were made more flexible, and product certification guidelines were made publicly accessible to simplify compliance.
Under Improving Credit Flow to MSMEs, loans have been linked to external benchmarks with shorter reset periods (3 months), the Mutual Credit Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs (MCGS-MSME) now provides cover up to ₹100 crore for equipment and machinery, Priority Sector Lending targets are enforced, collateral-free loans up to ₹10 lakh are available for micro and small enterprises, and working capital requirements for MSEs are set at a minimum of 20% of projected annual turnover for credit limits up to ₹5 crore.
Other MSME Reforms
The Budget 2025-26 expanded the MSME definition, raising investment and turnover limits to enhance confidence and generate employment for our youth, while credit guarantee cover for Micro and Small Enterprises doubled from ₹5 crore to ₹10 crore, improving access to formal finance for expansion and modernization, with higher limits and term loans for startups and exporters boosting growth and competitiveness.
Revised Thresholds:
- Micro: Investment up to ₹2.5 crore, turnover up to ₹10 crore
- Small: Investment up to ₹25 crore, turnover up to ₹100 crore
- Medium: Investment up to ₹125 crore, turnover up to ₹500 crore

GST 2.0 Reforms
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) reforms, represent another landmark step in reshaping India’s indirect tax framework to align with the aspirations of a young, entrepreneurial, and consumption-driven economy. The latest Next-Generation GST reforms, mark a decisive step towards simpler taxation, lower burden on citizens, and improved ease of doing business. They significantly strengthen GST’s role as a citizen-centric, business-friendly, and growth-oriented tax system.
- Simpler Tax Structure: The move to a two-slab GST regime (5% and 18%) reduces complexity, classification disputes, and compliance costs, improving ease of doing business, especially for MSMEs and small traders.
- Lower Cost of Living: Wide-ranging rate reductions on essential goods, household items, healthcare products, education materials, housing inputs, and services directly reduce inflationary pressures and enhance household affordability.
- MSME and Startup Enablement: Faster refunds, simplified registration and returns, and lower input costs aim is to boost the present businesses and startups and incentivise the youth to enter into businesses and initiate startups.
- Wider Tax Base and Revenue Stability: Simpler rates and improved compliance have expanded the GST taxpayer base to over 1.5 crore, while gross collections reached ₹22.08 lakh crore in FY 2024–25, reinforcing fiscal sustainability.
Overall, the Next-Generation GST reforms reinforce GST as a simpler, fairer, and growth-oriented tax system, delivering ease of living for consumers and ease of doing business for enterprises, while supporting consumption-led growth and long-term fiscal sustainability.

Export Promotion Mission
In a major boost to India’s trade competitiveness, the Union Cabinet approved the Export Promotion Mission (EPM) as a flagship structural reform with an outlay of ₹25,060 crore for FY 2025–26 to FY 2030–31. Announced in the Union Budget 2025–26, EPM marks a strategic shift from fragmented export support schemes to a single, outcome-based and digitally driven framework, aimed at empowering MSMEs, first-time exporters, and labour-intensive sectors. The Mission integrates financial support (Niryat Protsahan) including affordable trade finance and credit enhancement with non-financial enablers (Niryat Disha) such as quality compliance, branding, logistics, and market access.

The Mission
- Facilitates access to affordable trade finance for MSMEs,
- Enhances export readiness through compliance and certification support,
- Improves market access and visibility for Indian products,
- Boosts exports from non-traditional districts and sectors, and
- Generates employment across manufacturing, logistics, and allied services
It aims to position India’s export ecosystem for sustained, inclusive, and globally competitive growth in line with Viksit Bharat @2047.


Other Trade Reforms
During the year, trade and ease of doing business reforms focused on simplifying procedures, digitising interfaces, and reducing transaction costs, especially for MSMEs. Key measures included digital integration of trade systems (National Single Window, Trade Connect, ICEGATE, e-Commerce Export Hubs), Next Gen GST 2.0 with risk-based refunds, District Business Reform Action Plan (D-BRAP 2025) launched by DPIIT to decentralise approvals and inspections EoDB reforms, and MSME/start-up support across 154 targeted reforms.
Enhanced market access through GeM and MSME-SAMBANDH has strengthened MSME participation in Government procurement. Additionally, export incentives under the Foreign Trade Policy and disbursal of ₹58,000 crore under Remission of Duties and Taxes on Export Products scheme (till March 2025) have provided a further boost.

Driving Outcomes: Towards a Future-Ready Economy
Taken together, the year’s economic reforms reflect a clear shift towards outcome-based governance, reducing friction for citizens and businesses, enhancing transparency and efficiency, and laying the foundation for sustained, inclusive growth. By simplifying taxation, modernizing labour laws, strengthening MSMEs, boosting rural employment, and advancing digital payments, these measures collectively foster trust, resilience, and global competitiveness in India’s economy.
















